The Division of Responsibility in Feeding: Nurturing Healthy Eating Habits
In the realm of childhood nutrition, finding the right balance between parental guidance and children’s autonomy is key. The Division of Responsibility (DoR) in Feeding, developed by feeding expert Ellyn Satter, offers a framework that promotes healthy eating habits and a positive relationship with food. By understanding and implementing the principles of the DoR, parents can lay the foundation for their children to make informed choices and develop lifelong healthy eating habits.
The Role of Parents and/or Caregivers
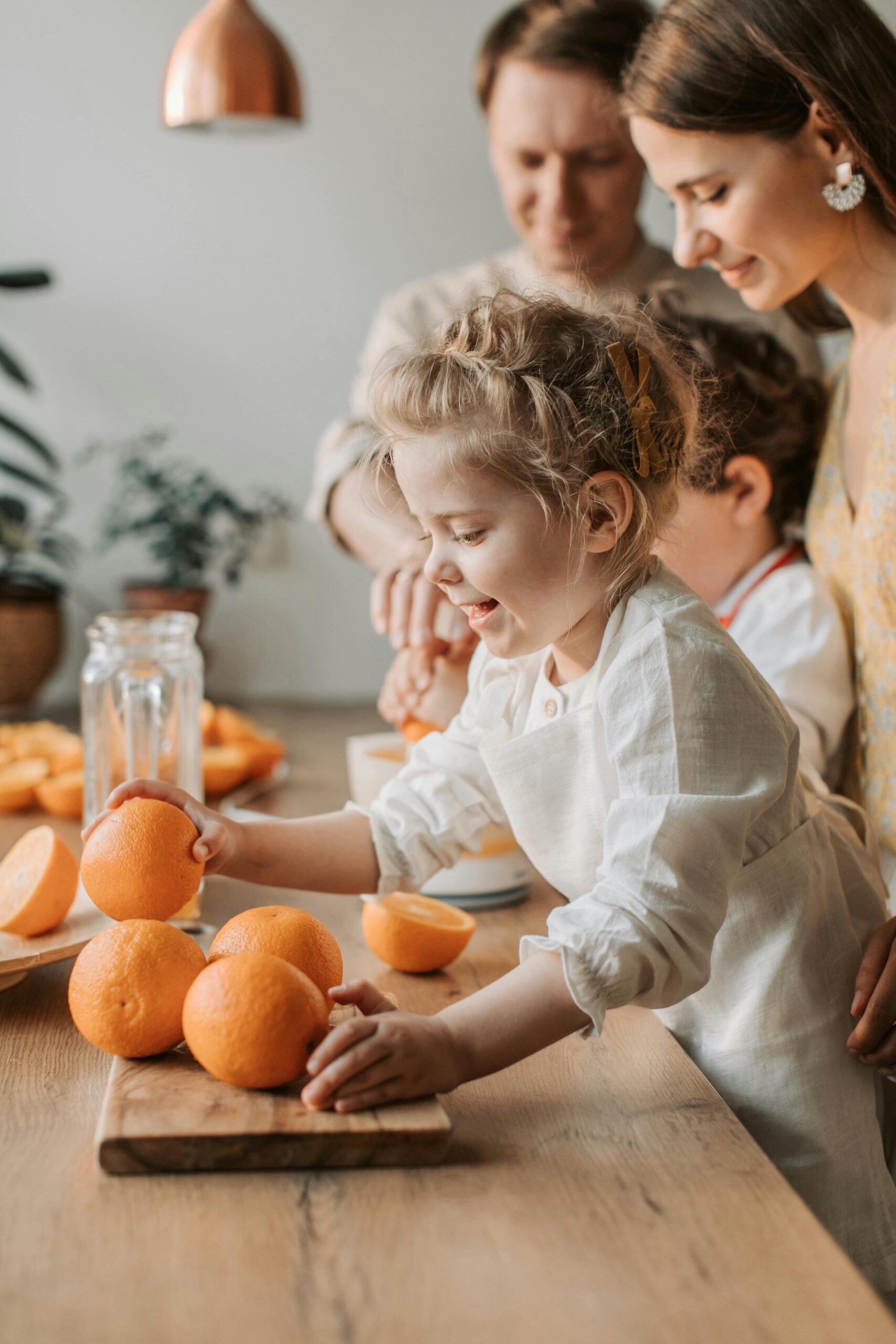
As parents, our responsibility lies in providing a nutritious food environment for our children. We determine what, when, and where meals and snacks are served. Offering a variety of wholesome foods, setting regular mealtimes, and establishing a positive meal atmosphere are important aspects of our role. By modeling healthy eating behaviors ourselves, we become powerful influencers in shaping our children’s eating habits.
Empowering Children’s Autonomy
Children also have a crucial role in the Division of Responsibility. They are responsible for deciding how much to eat and whether to eat at all. Encouraging them to listen to their hunger and fullness cues fosters self-regulation and develops a healthy relationship with food. This approach helps children develop trust in their own bodies and establish a balanced relationship with eating, free from external pressures or restrictions.
Creating a Positive Food Environment
A positive mealtime environment is crucial for nurturing healthy eating habits. Minimizing distractions, promoting positive conversation, and avoiding pressure or judgment are key elements. When mealtimes are enjoyable and relaxed, children develop a positive association with food and are more likely to explore new flavors and textures. Engaging children in meal planning and preparation can also boost their enthusiasm for healthy choices and foster a sense of ownership over their food decisions.
Building Resilience and Coping Skills
The Division of Responsibility teaches children valuable life skills beyond just healthy eating. By allowing them to make age-appropriate choices, children learn to navigate their preferences and make decisions independently. This approach also helps build resilience as they face various foods, textures, and tastes. Children gradually develop coping skills and become more open to trying new foods, contributing to a diverse and balanced diet.
Flexibility and Long-Term Benefits
The Division of Responsibility provides flexibility to accommodate individual preferences and needs. It recognizes that children’s appetites and preferences can vary from day to day and encourages parents to respect these variations. By implementing this approach consistently, parents can help their children establish a healthy relationship with food that lasts a lifetime, preventing issues such as disordered eating or excessive food restriction.
Conclusion
The Division of Responsibility in Feeding offers a valuable framework for parents seeking to promote healthy eating habits in their children. By understanding and implementing the DoR principles, parents can foster autonomy, build positive food environments, and empower their children to make informed choices. This approach not only nurtures healthy eating habits but also cultivates positive relationships with food, setting the stage for a lifetime of well-being and balanced nutrition.